Introduction
In today’s fast-paced software development landscape, the ability to deliver high-quality software quickly and efficiently is crucial for staying competitive. Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) have emerged as essential practices for achieving this goal. In this blog post, we will explore how to use CI/CD to improve your software delivery process, streamline development workflows, and ensure a seamless and automated path from code changes to production deployment.
What is CI/CD?
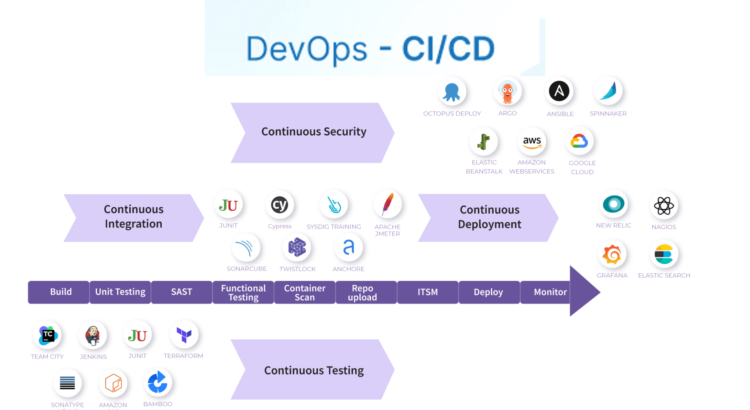
Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Delivery (CD) are software development practices that promote frequent and automated integration, testing, and delivery of code changes. CI focuses on merging code changes from multiple developers into a shared repository regularly, allowing for early detection and resolution of integration issues. CD builds upon CI by automating the process of deploying code changes to various environments, including testing, staging, and production.
The Benefits of CI/CD
-
Faster Feedback Loop: CI/CD shortens the feedback loop between writing code and seeing its impact, allowing developers to receive rapid feedback on the quality and functionality of their changes.
-
Automated Testing: Automated testing is an integral part of CI/CD, ensuring that code changes are thoroughly tested before deployment, reducing the risk of defects reaching production.
-
Consistency: CI/CD promotes consistency in the development process, as all code changes go through the same automated pipeline, ensuring uniformity and standardization.
-
Reduced Time to Market: By automating integration, testing, and deployment processes, CI/CD enables faster and more frequent releases, allowing you to deliver new features and bug fixes to users quickly.
Implementing CI/CD in Your Software Delivery Process
-
Version Control: Set up a version control system, such as Git, to manage your codebase. Ensure that all code changes are committed to the repository frequently.
-
Continuous Integration (CI):
-
Automate Code Integration: Use a CI server (e.g., Jenkins, GitLab CI/CD, CircleCI) to automatically merge code changes from different developers into a shared branch.
-
Automated Testing: Integrate automated testing (unit tests, integration tests, and other types of tests) into the CI pipeline to validate code changes.Continuous Delivery (CD):
-
Automated Deployment: Automate the process of deploying your application to various environments (testing, staging, production) using deployment scripts or containerization platforms like Docker and Kubernetes.
-
Configuration Management: Utilize configuration management tools to ensure consistency between environments and eliminate discrepancies.Monitoring and Feedback:Implement monitoring and logging solutions to track the performance and behavior of your application in real-time.Set up alerts to notify your team about potential issues or anomalies.Security and Compliance:Integrate security testing tools (e.g., SAST, DAST) into the CI/CD pipeline to identify and fix security vulnerabilities early in the development process.Ensure compliance with relevant regulations and best practices.
Best Practices for CI/CD
-
Automate Everything: Automate as much of the development and deployment process as possible to reduce manual intervention and human error.
-
Small, Frequent Changes: Encourage small, incremental changes to the codebase, as they are easier to test, review, and deploy.
-
Parallel Environments: Use parallel environments for testing and staging to ensure that new changes can be tested thoroughly before reaching production.
-
Versioned Artifacts: Use versioned artifacts for deployments to ensure consistency and rollback capability.
-
Collaboration and Communication: Foster collaboration and communication between development, testing, and operations teams to ensure a smooth CI/CD process.
Conclusion
CI/CD is a transformative approach to software delivery that empowers organizations to deliver high-quality software rapidly and reliably. By automating integration, testing, and deployment processes, CI/CD reduces manual effort, enhances consistency, and accelerates the time to market software products. Implementing CI/CD requires a thoughtful approach, incorporating automation, monitoring, security, and collaboration across the development lifecycle. By embracing CI/CD, you can improve your software delivery process, increase developer productivity, and deliver value to users efficiently and consistently.