Introduction
In the world of software development, the need for scalable and reliable applications has never been greater. Enter Docker, a revolutionary containerization platform that has transformed the way applications are developed, deployed, and managed. Docker provides a powerful solution to the challenges of scalability and reliability, allowing developers to create lightweight, portable containers that encapsulate applications and all their dependencies. In this blog post, we will explore how Docker unlocks the secret to scalable and reliable applications, revolutionizing the way software is built and deployed.
What is Docker and How Does it Work?
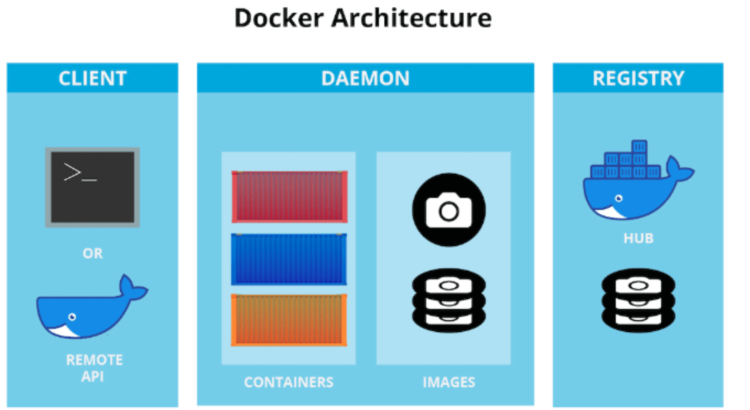
Docker is an open-source platform that enables developers to package applications and their dependencies into containers. Containers are self-contained units that include the application code, runtime, libraries, and other necessary components. These containers can run consistently across different environments, from development to production, ensuring that applications behave the same way regardless of the underlying infrastructure.
The Secret to Scalability
-
Isolation: Docker’s containerization provides a high degree of isolation between applications and their dependencies. Each container runs in its own isolated environment, preventing interference and conflicts with other containers. This isolation allows applications to scale horizontally by running multiple containers across multiple nodes.
-
Lightweight: Docker containers are lightweight and have minimal overhead compared to virtual machines. This efficiency allows organizations to run more containers on the same hardware, leading to improved resource utilization and cost-effectiveness.
-
Easy Scaling: Docker’s container orchestration tools, such as Kubernetes and Docker Swarm, enable easy scaling of containers based on demand. These tools automatically manage the deployment, scaling, and monitoring of containers, ensuring applications can adapt to fluctuating workloads.
-
Efficient Resource Utilization: Docker allows fine-grained control over resource allocation for containers, ensuring that each application gets the resources it needs without wasting valuable computing power.
The Secret to Reliability
-
Consistency: Docker containers ensure consistency across different environments, from development to production. Developers can be confident that applications will behave the same way in testing, staging, and production environments, reducing the risk of errors caused by environmental inconsistencies.
-
Version Control: Docker allows versioning of container images, enabling developers to roll back to a previous version if issues arise. This version control ensures that changes to applications can be managed effectively and rolled back if necessary, enhancing reliability.
-
Continuous Integration and Deployment (CI/CD): Docker integrates seamlessly with CI/CD pipelines, facilitating automated testing, continuous integration, and deployment. This streamlined process ensures that reliable and thoroughly tested containers are pushed to production, reducing the likelihood of defects.
-
Fault Tolerance: Docker’s containerization approach enhances the fault tolerance of applications. In the event of a container failure, orchestration tools can automatically spin up new containers to replace the failed ones, ensuring minimal downtime and continuous service availability.
Security and Compliance
-
Isolation and Sandboxing: Docker’s container isolation provides an extra layer of security, as each container has its own isolated environment. This containment prevents applications from interfering with each other, reducing the attack surface for potential security breaches.
-
Image Scanning and Vulnerability Management: Docker Hub and other container registries provide image scanning tools to identify security vulnerabilities and enforce compliance with security standards. This helps in ensuring that only secure and compliant images are used in the container environment.
Best Practices for Building a Docker Image
Here are some best practices to follow when building a Docker image:
-
Use a .dockerignore file: Use a .dockerignore file to exclude files and directories that are not needed in the Docker image. This helps to reduce the size of the context sent to the Docker daemon during the build process.
-
Use multistage builds: Use multistage builds to optimize your Docker image size. Multistage builds allow you to build multiple images in a single Dockerfile, which can help reduce the number of layers in your final image.
-
Minimize the number of layers: Minimize the number of layers in your Docker image to reduce the build time and image size. Each layer in a Docker image adds overhead, so it’s important to combine multiple commands into a single layer.
-
Use specific tags: Use specific tags for your Docker image instead of the latest tag. This helps to ensure that you have a consistent and reproducible environment.
-
Avoid installing unnecessary packages: Avoid installing unnecessary packages in your Docker image to reduce the image size and improve security.
-
Use COPY instead of ADD: Use the COPY command instead of ADD to copy files into your Docker image. The COPY command is more predictable and has fewer side effects than the ADD command.
-
Avoid using the root user: Avoid using the root user in your Docker image to improve security. Instead, create a non-root user and use that user in your Docker image.
-
Use a small base image: Use a small base image such as Alpine Linux or BusyBox while building an image Docker. This helps reduce the size of your final Docker image and improves security by minimizing the attack surface.
Conclusion
Docker has revolutionized the way software applications are developed, deployed, and managed. Its containerization technology has unlocked the secret to scalable and reliable applications, providing a robust solution to the challenges faced by modern software development. With Docker, developers can package applications and their dependencies into lightweight, portable containers that can run consistently across different environments. This level of scalability and reliability empowers organizations to scale their applications easily, respond to changing workloads, and deliver software with confidence. Docker’s impact on the software industry is profound, driving the adoption of containerization and changing the way applications are built and deployed in the dynamic and competitive landscape of modern technology.
Is your business struggling with Docker image issues in the development or production environment? Docker is a powerful tool for building and deploying applications, but it can also be complex and challenging to manage. Whether you’re facing issues with image compatibility, security vulnerabilities, or performance problems, it’s important to have a plan in place for resolving these issues quickly and effectively. Spundan provides end-to-end DevOps, Cloud, and DevSecOps solutions.